This site is intended for US healthcare professionals only.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION | FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION | AMNEAL.COM
PINWORM INFECTION CAN BE CHALLENGING TO FULLY ERADICATE1
Pinworm infection is spread from human to human by the ingestion of eggs. Gravid adult female pinworms migrate nocturnally into the perianal region and release thousands of microscopic eggs. The sticky eggs and the presence of migrating pinworms cause anal pruritus. Within hours, the eggs become highly infective and are transferred when an infected person scratches the perianal area. The eggs easily stick to fingertips and fingernails.2

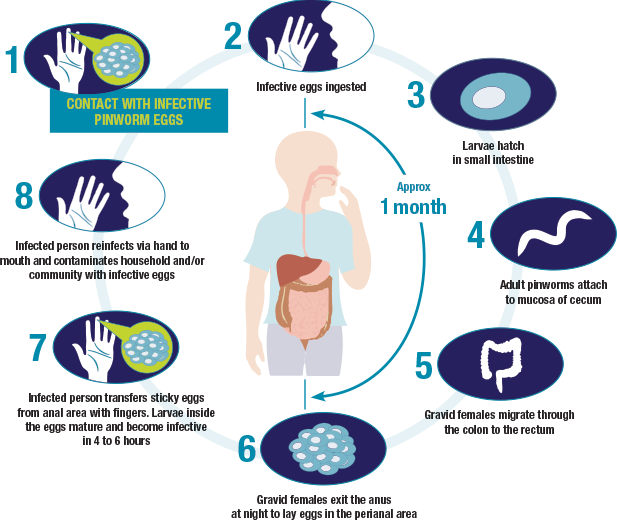
Self-infection and reinfection
Self-infection and reinfection can only occur if infective eggs are ingested, usually via hand to mouth. Infective eggs can survive up to 3 weeks on indoor fomites. Person-to-person transmission can occur through contact with fomites that have already been contaminated with pinworm eggs, such as bed linens, clothing, toilet handles, doorknobs, towels, furniture, carpeting, cell phones, remote controls, and other shared surfaces. The tiny eggs can also become airborne and inhaled or deposited onto food and swallowed, which can spread the infection.1,2
Pinworm life cycle and route of infection and reinfection2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindication: EMVERM is contraindicated in persons with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its excipients (mebendazole, microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, anhydrous lactose, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, stearic acid, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium saccharin, and FD&C Yellow #6).
Warnings and Precautions:
Risk of convulsions: Convulsions in infants below the age of 1 year have been reported
Hematologic effects: Neutropenia and agranulocytosis have been reported in patients receiving mebendazole at higher doses and for prolonged duration. Monitor blood counts in these patients
Metronidazole and serious skin reactions: Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) have been reported with the concomitant use of mebendazole and metronidazole
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials*: Anorexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, rash.
Adverse Reactions from Postmarketing Experience with Mebendazole*: Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, hypersensitivity including anaphylactic reactions, convulsions, dizziness, hepatitis, abnormal liver tests, glomerulonephritis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, exanthema, angioedema, urticaria, alopecia.
*Includes mebendazole formulations, dosages and treatment duration other than EMVERM 100 mg chewable tablet.
Drug Interactions: Concomitant use of EMVERM and metronidazole should be avoided.
Use in Specific Populations:
Pregnancy: Mebendazole use in pregnant women has not reported a clear association between mebendazole and a potential risk of major birth defects or miscarriages. However, there are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated helminthic infection during pregnancy.
Lactation: Limited data from case reports demonstrate that a small amount of mebendazole is present in human milk following oral administration. There are no reports of effects on the breastfed infant.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of EMVERM 100 mg chewable tablet has not been established in pediatric patients less than two years of age.
Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of mebendazole did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Overdosage: In patients treated at dosages substantially higher than recommended or for prolonged periods of time, the following adverse reactions have been reported: alopecia, reversible transaminase elevations, hepatitis, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms and signs of overdose: In the event of accidental overdose, gastrointestinal signs/symptoms may occur
Treatment of overdose: There is no specific antidote
Patient Counseling: Healthcare professionals should advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information). Advise patients that:
Taking EMVERM and metronidazole together may cause serious skin reactions and should be avoided.
EMVERM can be taken with or without food.
INDICATION
EMVERM is indicated for the treatment of patients two years of age and older with gastrointestinal infections caused by Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm), Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm), Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm), Necator americanus (hookworm), and Trichuris trichiura (whipworm).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Specialty, a division of Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information.
References:
1. American Academy of Pediatrics. Red Book: 2018-2021 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 31st ed. Itasca, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:634-635, 994. 2. Enterobiasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/enterobiasis/index.html. Updated December 8, 2017. Accessed March 5, 2019. 3. Maguire JH. Intestinal nematodes (roundworms). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:3199-3207.e2.

IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindication: EMVERM is contraindicated in persons with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its excipients (mebendazole, microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, anhydrous lactose, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, stearic acid, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium saccharin, and FD&C Yellow #6).
Warnings and Precautions:
Risk of convulsions: Convulsions in infants below the age of 1 year have been reported
Hematologic effects: Neutropenia and agranulocytosis have been reported in patients receiving mebendazole at higher doses and for prolonged duration. Monitor blood counts in these patients
Metronidazole and serious skin reactions: Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) have been reported with the concomitant use of mebendazole and metronidazole
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials*: Anorexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, rash.
Adverse Reactions from Postmarketing Experience with Mebendazole*: Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, hypersensitivity including anaphylactic reactions, convulsions, dizziness, hepatitis, abnormal liver tests, glomerulonephritis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, exanthema, angioedema, urticaria, alopecia.
*Includes mebendazole formulations, dosages and treatment duration other than EMVERM 100 mg chewable tablet.
Drug Interactions: Concomitant use of EMVERM and metronidazole should be avoided.
Use in Specific Populations:
Pregnancy: Mebendazole use in pregnant women has not reported a clear association between mebendazole and a potential risk of major birth defects or miscarriages. However, there are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated helminthic infection during pregnancy.
Lactation: Limited data from case reports demonstrate that a small amount of mebendazole is present in human milk following oral administration. There are no reports of effects on the breastfed infant.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of EMVERM 100 mg chewable tablet has not been established in pediatric patients less than two years of age.
Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of mebendazole did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Overdosage: In patients treated at dosages substantially higher than recommended or for prolonged periods of time, the following adverse reactions have been reported: alopecia, reversible transaminase elevations, hepatitis, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms and signs of overdose: In the event of accidental overdose, gastrointestinal signs/symptoms may occur
Treatment of overdose: There is no specific antidote
Patient Counseling: Healthcare professionals should advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information) Advise patients that:
Taking EMVERM and metronidazole together may cause serious skin reactions and should be avoided.
EMVERM can be taken with or without food.
INDICATION
EMVERM is indicated for the treatment of patients two years of age and older with gastrointestinal infections caused by Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm), Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm), Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm), Necator americanus (hookworm), and Trichuris trichiura (whipworm).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Specialty, a division of Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information.
